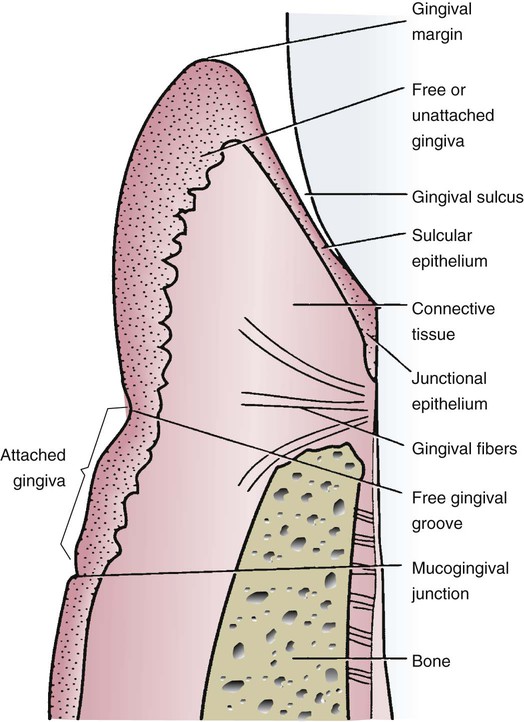
Gingival Wall . pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers. the periodontal pocket is a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus due to the apical migration of junctional epithelium. (1) to regain lost periodontal ligament. It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is about 1 mm wide in normal and healthy periodontium. reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either singly or in combination for three main purposes: they consist of mucosal tissue that covers the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible and finish at the neck of each tooth.
from pocketdentistry.com
reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either singly or in combination for three main purposes: pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. the periodontal pocket is a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus due to the apical migration of junctional epithelium. It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. they consist of mucosal tissue that covers the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible and finish at the neck of each tooth. (1) to regain lost periodontal ligament. the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is about 1 mm wide in normal and healthy periodontium. The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers.
8 Clinical Assessment Pocket Dentistry
Gingival Wall (1) to regain lost periodontal ligament. pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is about 1 mm wide in normal and healthy periodontium. they consist of mucosal tissue that covers the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible and finish at the neck of each tooth. It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers. the periodontal pocket is a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus due to the apical migration of junctional epithelium. (1) to regain lost periodontal ligament. reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either singly or in combination for three main purposes:
From www.semanticscholar.org
[PDF] Gingival esthetics An orthodontic and periodontal approach Gingival Wall pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is about 1 mm wide in normal. Gingival Wall.
From vdocuments.mx
Scanning electron microscopy of the gingival wall of deep periodontal Gingival Wall reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either singly or in combination for three main purposes: (1) to regain lost periodontal ligament. The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers. It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the. Gingival Wall.
From www.muhadharaty.com
1 pptx Dr. Hisham Muhadharaty Gingival Wall the periodontal pocket is a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus due to the apical migration of junctional epithelium. the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is about 1 mm wide in normal and healthy periodontium. pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. (1). Gingival Wall.
From www.researchgate.net
a Crescent shaped free gingival graft lightly pushes against gingival Gingival Wall reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either singly or in combination for three main purposes: (1) to regain lost periodontal ligament. the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is about 1 mm wide in normal and healthy periodontium. the periodontal pocket is a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus due to the apical. Gingival Wall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Gingival and Periodontal Disease PowerPoint Presentation, free Gingival Wall It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. they consist of mucosal tissue that covers the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible and finish at the neck of each tooth. pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of. Gingival Wall.
From www.researchgate.net
Structures of the gingiva and periodontium at various magnifications Gingival Wall The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers. (1) to regain lost periodontal ligament. It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is. Gingival Wall.
From www.dent-wiki.com
The gingiva Foundations of Periodontics The gingival epithelium Gingival Wall (1) to regain lost periodontal ligament. reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either singly or in combination for three main purposes: pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers. the marginal gingiva. Gingival Wall.
From drnenaddordevic.medium.com
Anatomy of the Oral cavity and salivary glands by Dr Nenad Dordevic Gingival Wall pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers. they consist of mucosal tissue that covers the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible and finish at the neck of each tooth. the. Gingival Wall.
From www.muhadharaty.com
principles of cavity preparation pptx dr.huda Muhadharaty Gingival Wall It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is about 1 mm wide in normal. Gingival Wall.
From www.kenhub.com
Gingiva Types, histology and clinical aspects Kenhub Gingival Wall (1) to regain lost periodontal ligament. pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either singly or in combination for three main purposes: the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is about 1 mm wide in normal. Gingival Wall.
From www.researchgate.net
Schematic drawing of the oral cavity [97]. Download Scientific Diagram Gingival Wall pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. they consist of mucosal tissue that covers the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible and finish at the neck of each tooth. the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is about 1 mm wide. Gingival Wall.
From pocketdentistry.com
11. Periodontium Periodontal ligament Pocket Dentistry Gingival Wall the periodontal pocket is a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus due to the apical migration of junctional epithelium. It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. they consist of mucosal tissue that covers the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible and finish at the. Gingival Wall.
From what-when-how.com
Orofacial Complex Form and Function (Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Gingival Wall It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. the marginal gingiva is the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus, it is about 1 mm wide in normal and healthy periodontium. the periodontal pocket is a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus due to the apical. Gingival Wall.
From www.researchgate.net
Score 3 for gingival wall, Score 0 for occlusal wall Download Gingival Wall The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers. pocket formation starts as an inflammatory change in the connective tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. the periodontal pocket is a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus due to the apical migration of junctional epithelium. reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either. Gingival Wall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Dental Terminology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Gingival Wall The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers. It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either singly or in combination for three main purposes: the marginal gingiva is. Gingival Wall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT PERIODONTAL POCKET PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Gingival Wall (1) to regain lost periodontal ligament. the periodontal pocket is a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus due to the apical migration of junctional epithelium. The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers. It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination. Gingival Wall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Dental Terminology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Gingival Wall the periodontal pocket is a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus due to the apical migration of junctional epithelium. It may occur due to coronal movement of the gingival margin, apical displacement of epithelial attachment or a combination of the above. reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either singly or in combination for three main purposes: The cellular and fluid. Gingival Wall.
From quizlet.com
Chapter 2 Gingival Landmarks 1 Diagram Quizlet Gingival Wall reconstructive or regenerative techniques are used either singly or in combination for three main purposes: they consist of mucosal tissue that covers the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible and finish at the neck of each tooth. The cellular and fluid inflammatory exudate causes degeneration of the surrounding connective tissue, including the gingival fibers. the marginal. Gingival Wall.